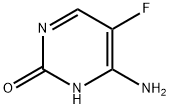
5-Fluorocytosine:Introduction and Indication
Oct 20,2023
Significant advances in antifungal therapy have been achieved during the past few decades with the introduction of new generations of antifungal agents, improved fungal diagnostics, and standardization of in vitro susceptibility testing. However, the management and appropriate treatment of fungal infections remain challenging due to the emergence of antifungal resistance.
5-Fluorocytosine (5-FC) is one of the earliest antifungal agents, initially synthesized in 1957 as an anticancer drug. Unlike 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), a closely related fluorinated pyrimidine, 5-FC does not exhibit antineoplastic activity but was found to possess antifungal activity. The compound has been used since 1968 to treat human cryptococcosis and candidiasis.

Introduction
5-Fluorocytosine is active against certain yeasts and some filamentous fungi. The drug is particularly significant for the treatment of fungal infections at body sites with limited drug penetration of other antifungal agents, such as infections of the urinary tract, brain, eyes, or heart valves. Effective therapy of fungal infections in these sanctuary sites is challenging, as other drug classes show limited penetration. The use of 5-FC as a monotherapy, however, is limited due to the rapid emergence of resistance and is only recommended for certain cases. When administered in combination with amphotericin B, 5-FC has become the gold standard for treating cryptococcal meningitis and complex Candida infections. Although resistance to 5-FC is well known, the genetic basis of resistance regulation has remained unknown. Understanding these mechanisms may help in discovering novel ways to reduce or reverse resistance and broaden the clinical use of this drug, benefiting from its excellent tissue distribution. In recent years, several studies have revisited this classic drug to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of resistance in different fungi.
Indication
5-Fluorocytosine is clinically licensed for the treatment of cryptococcosis, chromoblastomycosis, and aspergillosis. It is primarily used as a first-line therapy for the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis, often administered in combination with amphotericin B as induction therapy. The addition of 5-FC to amphotericin B has been shown to result in faster sterilization of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
The combination of 5-Fluorocytosine with fluconazole also achieves a similar effect compared to fluconazole monotherapy and is non-inferior to amphotericin B-based therapy for two weeks. This combination therapy is particularly recommended in areas where amphotericin B is not available.
One of the advantages of 5-FC is that it is well tolerated and can be administered orally. It has also been shown to prevent treatment failure by suppressing the amplification of hetero-resistance to fluconazole.
In addition to its use in cryptococcal meningitis, 5-Fluorocytosine is used as an adjunctive treatment with amphotericin B or fluconazole in complex systemic fungal infections, including septicemia, endocarditis, meningitis, or pulmonary infections caused by susceptible strains of Candida or Cryptococcus. 5-FC monotherapy is limited to the treatment of Candida cystitis in cases of fluconazole resistance, as 5-FC demonstrates high urinary concentrations. It is also effective in the treatment of chromoblastomycosis caused by various melanized fungi.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- What is flucytosine used to treat? Jan 25, 2024
Flucytosine has proved very effective in the treatment of Candida fungemia and systemic candidoses (but not mucocutaneous candidiasis) in combination with amphotericin B.
- Capecitabine Intermediate 1 Aug 16, 2023
5-Fluorocytosine also called Capecitabine Intermediate 1 is an orally active antifungal agent with a very narrow spectrum of activity.
- Mechanism and Side-effects of Flucytosine Mar 31, 2022
Flucytosine (Ancotil, Ancobon) is a fluorinated pyrimidine analog that is primarily used in combination with amphotericin B or fluconazole for the treatment of invasive yeast infections. Rapid emergence of drug resistance is observed when t
2,3,5-Tri-O-benzyl-D-ribonolactone is a key compound in the synthesis of important drugs, but requires careful handling due to its acute toxicity.....
Oct 20,2023API17-AAG is an Hsp90 inhibitor. This compound is a synthetic analog of geldanamycin, an antibiotic first purified in 1970 from Streptomyces hygroscopicus.....
Oct 20,2023APIFluorocytosine
2022-85-7You may like
- Fluorocytosine
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2024-06-07
- CAS:2022-85-7
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100
- Fluorocytosine
-

- $30.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-07
- CAS:2022-85-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 98%
- Supply Ability: 2000kg
- Flucytosine;5-Fluorocytosine
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-18
- CAS:2022-85-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10000kg