Antioxidant effects and research of Trolox
May 9,2024
What is Trolox?
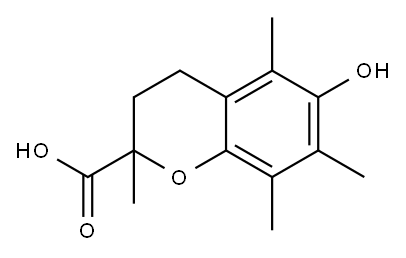
Trolox is a hydrophilic analogue of vitamin E. Trolox has been used as a standard antioxidant in antioxidant capacity assays. It has antioxidant, free radical scavenging, neuroprotective, lipid peroxidation, cell damage protection, Wnt signalling and iron death inhibition properties. The Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity (TEAC) assay can be used to measure the antioxidant capacity of foods, beverages and nutritional supplements.

Antioxidant and membranoprotective properties of trolox
In vitro studies have shown that trolox possesses antioxidant properties that inhibit ascorbic acid-dependent lipid peroxidation of liver homogenates and iron(2+)-induced chemiluminescence of egg yolk lipids. In addition, trolox has broad-spectrum antiradical activity, interacting with the stable free 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical, thereby reducing the generation of luminescent phenol radicals and reactive oxygen species, and binding to peroxyl radicals. Trolox also possesses membrane-protective properties, which reduce oxidative haemolysis of erythrocytes.
The effects of Trolox treatment on experimental strangulation ileus
Intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury is a serious and widespread clinical problem. Trolox effectively prevents lipid peroxidation in oxidative stress and protects cell injury. The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of Trolox alone on the intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in strangulation ileus model, which has not been investigated previously.
Methods: Twenty-eight Sprague-Dawley rats randomly divided into four groups were used. Group Laparotomy + Physiological Saline underwent laparotomy and was administered physiological saline; Group Laparotomy + Trolox was administered Trolox. Group Strangulation + Physiological Saline was administered physiological saline before reperfusion following strangulation ileus; Group Strangulation + Trolox was administered Trolox.
Results: Histopathological study was evaluated and catalase, malondialdehyde, superoxide dismutase measurements were performed in intestinal samples. Serum biochemistry parameters were evaluated. The higher grade (grade > or = 2) was significantly observed to decrease in Group Strangulation + Trolox when compared with Group Strangulation + Physiological Saline (p = 0.04). In Group Laparotomy + Trolox, when compared with Group Laparotomy + Physiological Saline, the higher grade was found to be significantly lower (p = 0.03). The catalase values were found to be significantly lower in Group Strangulation + Trolox, when compared with Group Strangulation + Physiological Saline, and in Group Laparotomy + Trolox, when compared with Group Laparotomy + Physiological Saline (p < 0.01).
Conclusions: Trolox is a powerful antioxidant as well as effectively prevents ischemia-reperfusion injury of the strangulated intestine segment.
The beneficial effect of trolox on sepsis-induced hepatic drug metabolizing dysfunction
The aim of this study was to investigate its effects on hepatic injury, especially alteration in cytochrome P450 (CYP)-dependent drug metabolism during polymicrobial sepsis. Rats were subjected to polymicrobial sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). The rats were treated intravenously with Trolox (2.5 mg/kg) or vehicle, immediately after CLP Serum aminotransferases and lipid peroxidation levels were markedly increased 24 h after CLP. This increase was attenuated by Trolox. Total CYP content and NADPH-P450 reductase activity decreased significantly 24 h after CLP. This decrease in CYP content was attenuated by Trolox. At 24 h after CLP, there was a significant decrease in the activity of these CYP isozymes: CYP1A1, 1A2, 2B1, and 2E1. However, Trolox differentially inhibited the decrease in CYP isozyme activity. Trolox had little effect on the decrease in CYP1A1 activity but Trolox significantly attenuated decreases in CYP1A2 and 2E1 activities. In fact, Trolox restored CYP2B1 activity to the level of activity found in control rats. Our findings suggest that Trolox reduces hepatocellular damage as indicated by abnormalities in hepatic drug-metabolizing function during sepsis. Our data also indicates that this protection is, in part, caused by decreased lipid peroxidation.
Scavenging effect of Trolox released from brushite cements
In this study a brushite cement was doped with the chain-breaking antioxidant Trolox. The effect of the antioxidant on the physical properties of the cement was evaluated and the release of Trolox was monitored by UV spectroscopy. The ability of the Trolox set free to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) released by macrophages was determined in vitro using a luminol-amplified chemiluminescence assay. Trolox did not modify the crystalline phases of the set cement, which mainly formed crystalline brushite after 7 days in humid conditions. The setting time, compressive strength and morphology of the cement also remained unaltered after the addition of the antioxidant. Trolox was slowly released from the cement following a non-Fickian transport mechanism and nearly 64% of the total amount was released after 3 days. Moreover, the capacity of Trolox to scavenge the ROS released by macrophages increased in a dose-dependent manner. Trolox-loaded cements are expected to reduce some of the first harmful effects of acute inflammation and can thus potentially protect the surrounding tissue during implantation of these as well as other materials used in conjunction.
References:
[1] E V TIBIR’KOVA A A S; V A Kosolapov. [Antioxidant and membranoprotective properties of trolox].[J]. Eksperimental”naya i Klinicheskaya Farmakologiya, 2009.
[2] B R KARAKAŞ. The effects of Trolox treatment on experimental strangulation ileus.[J]. Acta Chirurgica Belgica, 2012. DOI:10.1080/00015458.2012.11680867.
[3] GEMMA MESTRES . Scavenging effect of Trolox released from brushite cements[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2015. DOI:10.1016/j.actbio.2014.09.007.
[4] SANG-WON PARK; Sun M L. The beneficial effect of trolox on sepsis-induced hepatic drug metabolizing dysfunction[J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 2004. DOI:10.1007/BF02980111.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium is a dark-purple solid. It is insoluble in water. Soluble in chlorinated solvents, benzene, and THF.....
May 9,2024Catalyst and AuxiliaryMelamine is an inexpensive synthetic compound that becomes melamine resin when combined with formaldehyde. This melamine formaldehyde resin is used to make melamine dishware and hard plastic tableware.....
May 9,2024Organic reagentsTrolox
53188-07-1You may like
- Trolox
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2023-10-26
- CAS:53188-07-1
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month
- 6-HYDROXY-2,5,7,8-TETRAMETHYLCHROMAN-2-CARBOXYLIC ACID
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2023-09-06
- CAS:53188-07-1
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg
- (+/-)-6-Hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchromane-2-carboxylic acid 97%
-

- $15.00 / 1KG
- 2021-07-02
- CAS:53188-07-1
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%+ HPLC
- Supply Ability: Monthly supply of 1 ton