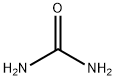
The Molecular Structure and Properties of Urea
Dec 28,2023
Urea is a vital organic compound used extensively in various industries due to its unique molecular structure and properties. Understanding its structure is key to comprehending its reactivity and widespread applications. In this article, we will explore the structural characteristics of urea and how they contribute to its polar nature, solubility, and reactivity.

Planar Structure
Urea's molecular structure consists of a carbonyl group and an amino group arranged in a planar hexagonal ring. This arrangement ensures that the carbonyl group and amino group lie on the same plane, resulting in a flat, planar structure.
Polar Molecules
Both the amino group (-NH2) and the carbonyl group (C=O) in the urea molecule are polar functional groups. These polar groups contribute to the polarity of urea as a whole, making it a polar molecule.
Hydrogen Bonding
Urea molecules possess the ability to form hydrogen bonds due to the presence of amino and carbonyl groups. The hydrogen atoms attached to each amino group (-NH3) can form hydrogen bonds with the oxygen atom of the carbonyl group (C=O). These intermolecular hydrogen bonds play a significant role in the properties and applications of urea.
Solubility in Water
The polar nature and hydrogen bonding capabilities of urea make it highly soluble in water. When dissolved in water, urea forms hydrogen bonds with water molecules, creating hydrogen bond networks. This increased solubility is essential for its application in various processes.
Reactivity
The amino and carbonyl groups in the urea molecule exhibit high reactivity. The amino groups can participate in chemical reactions such as acid-base reactions, while the carbonyl group is involved in reactions with aldehydes, ketones, and other compounds. These reactive groups make urea widely utilized in the chemical industry.
Conclusion
Urea's molecular structure yields several critical properties, including its planar arrangement, polarity, the formation of hydrogen bonds, and its enhanced solubility in water. These characteristics not only influence the chemical properties of urea but also drive its extensive applications in various industries. The reactivity of the amino and carbonyl groups expands urea's scope, enabling it to be used in many chemical reactions. Overall, understanding the molecular structure of urea provides insights into its functional properties and diverse utility across different fields.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- The role of urea in skin care Dec 14, 2023
Urea is a naturally occurring humectant agent that is part of the water-soluble fraction of the stratum corneum.
- Urea: Application, toxicity, storage, Preparation Apr 23, 2023
Urea is a key compound in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds in mammals and is produced naturally in the liver as a waste product of protein metabolism.
- Urea- a Versatile Nitrogenous Compound Nov 18, 2019
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two –NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group. It is also a carbonyl group with two C-bound amine groups.
Kojic acid is a small organic molecule with many potential applications, from pharmaceuticals to biopolymers and cosmetics.....
Dec 28,2023APIFruquintinib, a highly potent and selective vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGFR)-1, -2, and -3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor.....
Dec 28,2023InhibitorsUrea
57-13-6You may like
- Urea
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-31
- CAS:57-13-6
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: More than 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000KG/Month
- Urea
-

- $400.00 / 1Tons
- 2024-05-30
- CAS:57-13-6
- Min. Order: 1Tons
- Purity: 99.99%
- Supply Ability: 200tons
- Urea
-

- $63.00 / 1ton
- 2024-05-30
- CAS:57-13-6
- Min. Order: 10ton
- Purity: 46%
- Supply Ability: 5000tons