시아나이드 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
화학적 성질
Cyanides comprise a wide range of compounds, all of which have a CN molecule and exist in either a solid, liquid, or gaseous form. Physical characteristics range froma colorless or pale blue liquid with a faint bitter almond-like odor (hydrogen cyanide, HCN) to a white solid, powder, or crystalline hygroscopic salt (sodium cyanide, NaCN) to a colorless toxic gas also with an almond-like odor (cyanogens, NCCN). Cyanide compounds are either organic or inorganic. Organic cyanides contain a noncovalent CN functional group and are typically called the cyano group or nitriles. A common nitrile is methyl cyanide, also known as acetonitrile (CH3CN). Inorganic cyanides have a negatively charged polyatomic cyanide ion (CN) and are generally referred to as cyanides. This group includes the cyanide salts (i.e., sodium cyanide, NaCN) which are considered the most toxic form.
KCN and NaCN are white crystalline solids with a faint almond odor. Sodium cyanide also has a slight odor of hydrocyanic acid when damp. KCN: boiling point=1625℃ ; freezing/melting point=634℃ . NaCN: boiling point 1496℃; freezing/melting point=564℃ . NFPA 704 M Hazard identification (KCN and NaCN): Health 3, flammability 0 , reactivity 1. Soluble in water; slow decomposition releases highly toxic and flammable hydrogen cyanide gas.
용도
Cyanide, standard solution is used to dissolve metals and their ores. It is also used in clinical chemistry and in waste water treatment facilities to determine the concentration of dissolved and particulate materials.
생산 방법
Hydrogen cyanide is generally produced at point of use.
Production is covered under 40 CFR 415.420, applicability;
description of the hydrogen cyanide production subcategory.
정의
ChEBI: A pseudohalide anion that is the conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide.
일반 설명
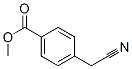
Aqueous solutions with a faint odor of bitter almonds. Toxic by skin absorption, by ingestion, and inhalation of the hydrogen cyanide from the decomposition of the material. Toxic oxides of nitrogen are produced in fires involving Methyl4-(cyanomethyl)benzoate. Obtain the technical name of the material from the shipping papers and contact CHEMTREC, 800-424-9300 for specific response information.
공기와 물의 반응
Water soluble. Inorganic cyanides react slowly with water to evolve gaseous hydrogen cyanide (HCN).
반응 프로필
CYANIDE SOLUTIONS slowly evolve hydrogen cyanide, a flammable and poisonous gas. Acids cause the rapid evolution of HCN. Carbon dioxide from the air is sufficiently acidic to liberate HCN from solutions of cyanides. Incompatible with isocyanates, nitrides, and peroxides. Mayinitiate polymerization reactions of epoxides. May react exothermically with metal salts to produce explosive products or evolve gaseous hydrogen.
위험도
Cellular asphyxiation, respiration inhibition, highly toxic; very poisonous.
건강위험
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or contact (skin, eyes) with vapors, dusts or substance may cause severe injury, burns or death. Reaction with water or moist air will release toxic, corrosive or flammable gases. Reaction with water may generate much heat that will increase the concentration of fumes in the air. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
화재위험
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Vapors may accumulate in confined areas (basement, tanks, hopper/tank cars etc.). Substance will react with water (some violently), releasing corrosive and/or toxic gases and runoff. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated or if contaminated with water.
Safety Profile
Very poisonous by
most routes. Cyanide directly stimulates the
chemoreceptors of the carotid and aortic
bodies with a resultant hyperpnea (increase
in the depth and rate of respiration). Cardac
irregularities are often noted, but the heart
invariably outlasts the respirations. Death is
due to respiratory arrest of central origm. It
can occur withn seconds or minutes of the
inhalation of htgh concentrations of HCN
gas. Because of slower absorption, death
may be more delayed after the ingestion of
cyanide salts, but the critical events sdl
occur within the first hour. Two other
sources of cyanide have been responsible for
human poisoning: the naturally occurring
amygdalin and the drug nitroprusside.
Amygdalin is a cyanogenic glycoside found
in apricot, peach, and similar fruit pits and in
sweet almonds (Sayre and Kaymakcalan,
잠재적 노출
Sodium and potassium cyanides are
used primarily in the extraction of ores, electroplating,
metal treatment, and various manufacturing processes.
Iodine cyanide: Used generally for destroying all lower
forms of life; in taxidermy to preserve insects, etc.
Carcinogenicity
There is no evidence that exposure
to cyanide causes cancer. USEPA lists cyanide as not
classifiable with respect to its potential to cause cancer in
humans. However, certain compounds included in the cyanide
group may be human carcinogens. For example, acrylonitrile
has been judged to be a probable human carcinogen.
Details of these effects are provided in the appropriate
sections where individual compounds are discussed.
운송 방법
UN1588 Cyanides, inorganic, solid, n.o.s.,
Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
UN1935
비 호환성
Soluble in water; slow decomposition
releases highly toxic and flammable hydrogen cyanide gas.
The aqueous solution of potassium and sodium cyanide are
highly corrosive, and strong bases. KCN and NaCN react
violently with acids, releasing highly flammable hydrogen
cyanide. Potassium and sodium cyanide are incompatible
with strong oxidizers (such as acids, acid salts; chlorates,
nitrates), organic anhydrides; isocyanates, alkylene oxides;
epichlorohydrin, aldehydes, alcohols, glycols, phenols, cre-
sols, caprolactum. Attacks aluminum, copper, zinc in the
presence of moisture. KCN and NaCN absorb moisture
from the air forming a corrosive syrup.
폐기물 처리
Consult with environmental
regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal
practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant
(≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing
storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. In
accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for
the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be
disposed properly by following package label directions or
by contacting your local or federal environmental control
agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office. Add
strong alkaline hypochlorite and react for 24 hours. Then
flush to sewer with large volumes of water
.
시아나이드 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품