|
|
| | LEAD (II) O-PHOSPHATE Basic information |
| Product Name: | LEAD (II) O-PHOSPHATE | | Synonyms: | LEAD(II)PHOSPHATE(3:2);Lead orthophosphate;LEAD PHOSPHATE;LEAD PHOSPHATE TRIBASIC;LEAD (II) O-PHOSPHATE;Phosphoric acid, lead(2+) salt (2:3);DIBASICLEADPHOSPHATE;C.I.77622 | | CAS: | 7446-27-7 | | MF: | O8P2Pb3 | | MW: | 811.54 | | EINECS: | 231-205-5 | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 7446-27-7.mol | 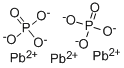 |
| | LEAD (II) O-PHOSPHATE Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 1014° | | density | 6.9 | | solubility | insoluble in H2O, ethanol | | form | white hexagonal crystals | | color | white hexagonal, hexane crystals, crystalline | | Water Solubility | g/L H2O: 1.35×10?4 (20°C) [KRU93] | | Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 42.1 | | EPA Substance Registry System | Lead(II) phosphate (7446-27-7) |
| | LEAD (II) O-PHOSPHATE Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | Lead phosphate is white powder soluble in acids and alkalis. Lead (II) phosphate is insoluble
in water and alcohol but soluble in nitric acid and has fixed alkali hydroxides. On
heating, it decomposes and emits very toxic fumes containing Pb and POx.
Reports have indicated that on the basis of sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental
animals and inadequate evidence for the carcinogenicity in humans, lead acetate
and lead phosphate are reasonably anticipated to be human carcinogens. Information on
the toxicology profile of lead phosphate is limited. | | Chemical Properties | Lead phosphate is a white powder or colorless
crystals. | | Uses | Stabilizer for styrene and casein plastics; in special glasses. | | General Description | White powder. | | Air & Water Reactions | Insoluble in water, soluble in acids and alkalis. | | Reactivity Profile | Salts, basic, such as LEAD (II) O-PHOSPHATE, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. | | Potential Exposure | Lead phosphate is used as a stabilizer
in styrene and casein plastics | | First aid | If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Antidotes and special procedures for lead: Persons with significant lead poisoning are sometimes treated with CaEDTA while hospitalized. This “chelating” drug causes arush of lead from the body organs into the blood and kidneys, and thus has its own hazards, and must be administered only by highly experienced medical personnel undercontrolled conditions and careful observation. Ca EDTA orsimilar drugs should never be used to prevent poisoningwhile exposure continues or without strict exposure control,as severe kidney damage can result.Note to physician: For severe poisoning BAL [British AntiLewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol (C3H8OS2)] has beenused to treat toxic symptoms of certain heavy metals poisoning. In the case of lead poisoning it may have SOMEvalue. Although BAL is reported to have a large margin ofsafety, caution must be exercised, because toxic effects maybe caused by excessive dosage. Most can be prevented bypremedication with 1-ephedrine sulfate (CAS: 134-72-5). | | storage | Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from heat, oxidizers, strong acids.Lead is regulated by an OSHA Standard 1910.1025. Allrequirements of the standard must be followed. A regulated,marked area should be established where this chemical ishandled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHAStandard 1910.1045. | | Shipping | UN3288 Toxic solids, inorganic, n.o.s., Hazard
Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical
Name Required | | Incompatibilities | Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates,
nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine,
bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases,
strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, and active metals. | | Waste Disposal | Consult with environmental
regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal
practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant
(≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. |
| | LEAD (II) O-PHOSPHATE Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|