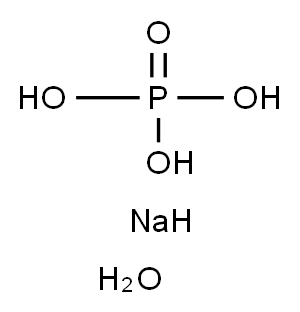
제일인산나트륨2수화물
|
|
제일인산나트륨2수화물 속성
- 녹는점
- 60 °C
- 밀도
- 1,915 g/cm3
- 저장 조건
- Store at +5°C to +30°C.
- 용해도
- H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, 투명, 무색
- 물리적 상태
- 고체
- 물리적 상태
- 단단한 모양
- 색상
- 하얀색
- 수소이온지수(pH)
- 4.0-4.5 (25℃, 50mg/mL in H2O)
- 냄새
- 냄새 없는
- pH 범위
- 4.2 - 4.5
- 수용성
- 녹는
- 감도
- Hygroscopic
- 최대 파장(λmax)
- λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.085
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.070
- Merck
- 14,8660
- 안정성
- 안정적인.
- InChIKey
- VBJGJHBYWREJQD-UHFFFAOYSA-M
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 13472-35-0(CAS DataBase Reference)
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
| 위험품 표기 | Xi | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 36-36/37/38 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 39-26-24/25-36 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 1 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | WA1900500 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS 번호 | 2835 22 00 | ||
| 독성 | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 8290 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit > 7940 mg/kg |
제일인산나트륨2수화물 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
약간 의 조해성이 있고 열을 가하면 100℃에서 무수물로 되고 강열하면 메타인산나트륨을 생성한다. 용해 도는 (20℃,112/100水),(99℃,448/100水),수용액은 약산성이다. 알코올에는 불용, 클로로포름 에는 약간 녹는다.용도
1. 청 관제 (일반 공업용 보일러)2. 염색 (염료 분산제)
3. 양모 탈색제
4. 의약 (페니실린, 스 트렙토 마이신의 배양제)
5. 식품 (식육 결착제)
화학적 성질
white crystalline solid용도
Sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate acts as buffering capacity reagent in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. It is used in the preparation of biological buffers. It is also used in the purification of antibodies, as a laxative and, in combination with other sodium phosphates.Sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate is a reagent with very high buffering capacity widely used in molecular biology, biochemistry and chromatography. Sodium phosphate dibasic is highly hygroscopic and water soluble.
Recommended chemicals for the preparation of phosphate buffers are sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate,NaH2PO4.2H2O(mol. wt.156.0),disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate,Na2HPO4.2H2O (mol. wt.178.0), and sodium hydroxide pellets.
생산 방법
Monobasic sodium phosphate is prepared by adding phosphoric acid to a hot, concentrated solution of disodium phosphate until the liquid ceases to form a precipitate with barium chloride. This solution is then concentrated and the monobasic sodium phosphate is crystallized.Pharmaceutical Applications
Monobasic sodium phosphate is used in a wide variety of pharmaceutical formulations as a buffering agent and as a sequestering agent. Therapeutically, monobasic sodium phosphate is used as a mild saline laxative and in the treatment of hypophosphatemia.Monobasic sodium phosphate is also used in food products, for example, in baking powders, and as a dry acidulant and sequestrant.
Safety
Monobasic sodium phosphate is widely used as an excipient in parenteral, oral, and topical pharmaceutical formulations.Phosphate occurs extensively in the body and is involved in many physiological processes since it is the principal anion of intracellular fluid. Most foods contain adequate amounts of phosphate, making hypophosphatemia virtually unknown except in certain disease states or in patients receiving total parenteral nutrition. Treatment is usually by the oral administration of up to 100 mmol of phosphate daily.
Approximately two-thirds of ingested phosphate is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, virtually all of it being excreted in the urine, and the remainder is excreted in the feces. Excessive administration of phosphate, particularly intravenously, rectally, or in patients with renal failure, can cause hyperphosphatemia that may lead to hypocalcemia or other severe electrolyte imbalances. Adverse effects occur less frequently following oral consumption, although phosphates act as mild saline laxatives when administered orally or rectally (2–4 g of monobasic sodium phosphate in an aqueous solution is used as a laxative). Consequently, gastrointestinal disturbances including diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting may occur following the use of monobasic sodium phosphate as an excipient in oral formulations. However, the level of monobasic sodium phosphate used as an excipient in a pharmaceutical formulation is not usually associated with adverse effects.
LD50 (rat, IM): 0.25 g/kg(10)
LD50 (rat, oral): 8.29 g/kg
저장
Monobasic sodium phosphate is chemically stable, although it is slightly deliquescent. On heating at 100°C, the dihydrate loses all of its water of crystallization. On further heating, it melts with decomposition at 205℃, forming sodium hydrogen pyrophosphate, Na2H2P2O7. At 250℃ it leaves a final residue of sodium metaphosphate, NaPO3.Aqueous solutions are stable and may be sterilized by autoclaving.
Monobasic sodium phosphate should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry place.
비 호환성
Monobasic sodium phosphate is an acid salt and is therefore generally incompatible with alkaline materials and carbonates; aqueous solutions of monobasic sodium phosphate are acidic and will cause carbonates to effervesce.Monobasic sodium phosphate should not be administered concomitantly with aluminum, calcium, or magnesium salts since they bind phosphate and could impair its absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Interaction between calcium and phosphate, leading to the formation of insoluble calcium phosphate precipitates, is possible in parenteral admixtures.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (injections; infusions; ophthalmic, oral, topical, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.제일인산나트륨2수화물 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
제일인산나트륨2수화물 공급 업체
글로벌( 342)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sichuan Shifang Jinda Chemical Co.,Ltd | +8613909025083 |
jinda@cn-jdchem.com | China | 1 | 58 |
| Chongqing Chuandong Chemical (Group) Co. Ltd. | +86-13637972665 +86-13637972665 |
wxc@cd1958.com | China | 81 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12468 | 58 |
| Henan Bao Enluo International TradeCo.,LTD | +86-17331933971 +86-17331933971 |
deasea125996@gmail.com | China | 2503 | 58 |
| airuikechemical co., ltd. | +undefined86-15315557071 |
sales01@airuikechemical.com | China | 994 | 58 |
| Ouhuang Engineering Materials (Hubei) Co., Ltd | +8617702722807 |
admin@hbouhuang.com | China | 3001 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | +8613343047651 |
admin@zlchemi.com | China | 2603 | 58 |
| Jiangsu Kolod Food Ingredients Co.,Ltd. | +86-518-85110578 +8618805133257 |
sales3257@jskolod.com | China | 132 | 60 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21688 | 55 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418679 +86-18949832763 |
info@tnjchem.com | China | 2989 | 55 |